Argentum, or silver, is a metal and chemical element assigned atomic number 47 in the periodic table. The chemical formula of the metal is Ag. Silver was explored by mankind back in the fourth millennium BC. The discovery of this metal did not require the help of scientists, since it was found by man as native silver. Moreover, the nuggets reached very impressive sizes. For example, in the fifteenth century a nugget weighing over 20 tons was mined.
However, mining silver required more effort than mining gold. For this reason, for several centuries, silver was more expensive than gold. The reserves of silver ore on Earth today amount to over 550 tons, and the leading countries in silver mining are considered to be:
- Peru.
- Australia.
- Chile.
- Mexico.
The precious metal is found in the Earth's crust in a concentration of 70 milligrams per ton. In nature, argentum is found in most cases in ore deposits in combination with other elements. There are over fifty types of silver ores in nature, but the following are considered effective from an economic point of view:
- native silver;
- kustelite;
- electrum;
- bromargerite;
- will be sad;
- aguilarite and others.
Silver can occur in nature together with gold, and this formation is called electrum. The noble metal is concentrated in large quantities in ores containing uranium, bismuth and nickel.
Silver crystals
Native silver is found in sulfide ores, in which it forms tiny crystals dispersed among the other metals of which the ores are composed. At the fractures, the crystals have an uneven angular surface, which makes them look like hooks. This is a find that is found in natural conditions much less often than gold. Moreover, the appearance of such nuggets is very unusual. Due to its plasticity, silver forms nuggets that resemble lattices, tubes, branches and strands. For this reason, such silver is not used for industrial purposes, but serves only as an exhibit in museums.
Silver, properties of the atom, chemical and physical properties.
Ag 47 Silver
107.8682(2) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s1
Silver is an element of the periodic system of chemical elements of D.I. Mendeleev with atomic number 47. It is located in the 11th group (according to the old classification - a secondary subgroup of the first group), the fifth period of the periodic system.
Silver atom and molecule. Silver formula. Structure of the silver atom
Silver price
Isotopes and modifications of silver
Properties of silver (table): temperature, density, pressure, etc.
Physical properties of silver
Chemical properties of silver. Interaction of silver. Chemical reactions with silver
Getting silver
Application of silver
Table of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev
Historical facts about silver
There is a legend that the first silver mines were discovered in 968 by none other than the founder of the Holy Roman Empire, the East Frankish king Otto I the Great. Legend has it that one day the king sent his huntsman into the forest to hunt. During the hunt, he tied the horse to a tree, which, while waiting for the owner, dug up the ground with its hooves, where there were unusual light stones. The emperor realized that this was silver and ordered a mine to be founded at this place. There is evidence that this rich mine was developed six centuries later. This is evidenced by the records of the German physician and metallurgist Georg Agricola (1494–1555). In general, Central Europe was very rich in deposits of silver nuggets. In Saxony in 1477, one of the largest nuggets in history was found weighing up to 20 tons! Millions of European coins were minted from silver mined in the Czech Republic, near the city of Joachimsthal. That’s why they were called “Joachimsthaler”; Over time, the word was shortened to "thaler". In Russia, this name was changed in its own way and here they were called “efimkas”. Silver thalers were the most common European coin in history, hence the modern name "dollar".
Czech Bohemian Joachimsthaler
European silver mines were so rich that silver consumption was measured in tons! But because The bulk of European silver mines were discovered in the 14th-16th centuries, but by now they have already been depleted. After the discovery of America, it turned out that this continent is very rich in silver. Its deposits have been discovered in Chile, Peru and Mexico. Argentina was even named after the Latin name for silver. Here we need to point out a very interesting fact. Geographical names of chemical elements were usually given to an element from the name of a place, for example, hafnium is named after the Latin name of the city of Copenhagen in which it was discovered, the elements polonium, ruthenium, gallium and others have geographical names. Just the opposite happened. The country was named after a chemical element! This is the only such case in history. Silver nuggets are still found in America today. One of them was discovered already in the 20th century in Canada. This nugget was 30 meters long and 18 meters deep! After mastering this nugget, it turned out that it contained 20 tons of pure silver!
Silver atom and molecule. Silver formula. Structure of the silver atom:
Silver (lat. Argentum) is a chemical element of the periodic system of chemical elements of D.I. Mendeleev with the designation Ag and atomic number 47. It is located in the 11th group (according to the old classification - a secondary subgroup of the first group), the fifth period of the periodic system.
Silver is a metal. Belongs to the group of transition metals, as well as precious metals and platinum group metals.
Silver is represented by the symbol Ag.
As a simple substance , silver under normal conditions is a malleable, ductile metal of a silvery-white color.
The silver molecule is monatomic.
The chemical formula of silver is Ag.
The electronic configuration of the silver atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s1. The ionization potential (first electron) of the silver atom is 731 kJ/mol (7.576234(25) eV).
Structure of the silver atom. The silver atom consists of a positively charged nucleus (+47), around which 47 electrons move through five shells. In this case, 46 electrons are in the internal level, and 1 electron is in the external level. Since silver is located in the fifth period, there are only five shells. First, the inner shell is represented by the s-orbital. The second - the inner shell is represented by s- and p-orbitals. The third and fourth - inner shells are represented by s-, p- and d-orbitals. The fifth - outer shell is represented by the s-orbital. At the outer energy level of the silver atom, there is one unpaired electron in the s orbital. In turn, the nucleus of a silver atom consists of 47 protons and 61 neutrons. Silver belongs to the elements of the d-family.
The radius of the silver atom (calculated) is 165 pm.
The atomic mass silver atom is 107.8682(2) a. eat.
Silver , being a noble metal, is characterized by relatively low reactivity.
Sulfur, atomic properties, chemical and physical properties
Silver in nature
Silver is a fairly rare element, containing only about 0.000001% in the lithosphere. This is about a thousand times less than the copper content in the earth's crust. Despite its rarity, silver is more often found in the form of nuggets, which is why it has been known since time immemorial. Nowadays, native silver has become rare; the bulk of silver is found in a variety of minerals, the main of which is argentite Ag2S. Also, most of it is found in the so-called polymetallic ores, in which silver is adjacent to metals such as lead, zinc and copper.
Historical reference
People have been familiar with silver since ancient times, as it was a popular nugget and did not require smelting ore. The oldest centers of metal mining and processing include prehistoric Sardinia, where it became known in the early Chalcolithic period.
Silver includes archaeological finds on different continents. Accessories dating back to 5.5–7 millennia were found on the territory of Ancient Egypt. The metal was then obtained from ancient deposits in Syria.
Since ancient times, the element has been assigned magical and healing properties. Because of this, it was associated with the Moon and was used by alchemists.
Silver is second only to gold in importance among precious metals. People learned to clean it about 2.5 thousand years ago. Previously, large mortars were used to grind ore to obtain a powder in which silver was separated from various impurities.
The value of the precious metal began to rise rapidly after the first coins were minted. This happened in Mesopotamia half a millennium BC. In Rus', payments were also made using silver - first, the required piece was cut off from a block of metal, then coins appeared.
Silver in nature
Finding pure metal is rare. Much of it consists of sulfites and shales. There are 60–70 mg (maximum 1 g) of the precious element per ton of rock.
It is profitable to extract silver from gold-silver, copper and lead ores. There are different connections:
- Electrum is a type of native gold that contains up to 50% silver. The compound is represented by lamellar formations or dendrites of white, light yellow, greenish color. It can be opaque, with a metallic sheen.
- Argentite is a silver-containing ore, a compound with sulfur. It occurs as a solid mass, in plates or crystals. It comes in iron-black or blackish-gray color. The connection is opaque and has a metallic luster.
- Galena is the most important source of lead. In addition to silver, it may contain cadmium, selenium and other impurities. It occurs in solid masses and cubic crystals. Characterized by lead-gray color, opacity and dull metallic luster.
- Proustite is an arsenic-silver blend. It is found in translucent solid masses of scarlet, crimson-red, reddish-gray color. Characterized by diamond shine and darkening in the light.
- Pyrargyrite is a relatively rare mineral, a compound with antimony, containing almost 60% silver. It is found in dendrites, granular inclusions, and plaque. It can be purple-red in color, translucent, translucent. Characteristic is a diamond semi-metallic luster.
- Stephanite (sour, brittle or black silver) - contains almost 70% precious metal, as well as sulfur and antimony. It occurs in solid masses and crystals of gray or black color.
The precious metal is also found in deposits of quartz, coal, oil, and polymetals. Sea water contains microscopic particles of silver, but it is difficult to extract it under such conditions, since the necessary technological base is missing. To obtain 1 g of metal you need 25 thousand tons of sea water.
A small amount of the element is contained in living organisms. The precious metal is also found in meteorites falling on the planet.
Scientists estimate that approximately 700 thousand tons of silver were mined. Even nuggets are not easy to recognize, since the metal is coated with a dark gray sulfide coating. Sometimes it resembles tangled wire or dry moss and is brownish or rusty in color. This effect is achieved by iron hydroxide coating the metal.
RESERVES AND PRODUCTION
Silver on acanthite, 2.3 x 1.8 x 1.1 cm, Peru, Uchucchacua mine
No large deposits are known in the USSR. Silver nuggets were previously found in the Turinsky mines in the Northern Urals, in a number of lead-zinc deposits in Altai, Kazakhstan, Eastern Siberia and other places. Of the foreign deposits, the following deposits were very famous: Kongsberg (Norway), where native silver was found to a depth of 900 m, Cobalt (Canada), Schneeberg (Germany). Mining of silver-containing ores can be done underground or open pit. First, using special instruments, prospectors check underground mines for minerals and precious metals. After discovering areas rich in silver, holes are made in appropriate places into which explosives are placed. The fragments of silver-containing ore raised by the explosion to the surface of the mine are crushed industrially. The precious metal is extracted from ore using the methods of amalgation and cyanidation.
STRUCTURE
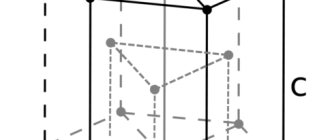
Crystal structure of silver
Cubic system; hexaoctahedral c. With. ZL 4 4L6 3 6L 2 9RS. Crystal structure. Face centered cube. The appearance of crystals. Properly formed crystals are very rare. Common forms: , . Doubles by (111). Aggregates. It is sometimes found in the form of typical “knitted” feathery dendrites, thin irregular plates and leaflets. Mossy, hair-like and wire-like forms are also characteristic. The most common grains are irregularly shaped and larger continuous clusters called nuggets.
How to distinguish from a fake
Silver is a noble, precious metal, which is often counterfeited by criminals and sold under its guise, at best, silver-plated metals or alloys with low argentum content. To identify a fake, it is necessary to use the properties of the metal, primarily thermal conductivity. Tie the product onto a thread and lower it into boiling water after 0.5-1 minutes. pull it out and feel it, the metal instantly becomes hot, unlike others.
The second method can also be used when buying silver, using a sharp object or needle (pin, sharp knife) to scratch the metal (scratch it) there should be no marks left on it.
The third way to identify precious metal or zinc is to apply iodine or a medicine with sulfur to the product; if the place is darkened, then it is a fake.
Silver never leaves marks on the skin, so in a jewelry store before purchasing, you need to rub the product over the skin; if dark stripes appear on it, then it is a fake or an alloy with a low argentum content.
The most elementary and simplest method is chalk, which is used to apply it to the decoration. Chalk is the only material on which dark traces of silver remain.
When purchasing silver products, you need to choose trusted jewelry stores, and also take into account the current price of silver on the market, which will allow you to identify a fake.
Application of silver
Since ancient times, silver has been used in the manufacture of mirrors; nowadays it is being replaced with aluminum to reduce the cost of production. The low electrical resistance of silver is used in electrical engineering and electronics, where various contacts and connectors are made from it. Currently, silver is practically not used for the production of coins; only commemorative coins are made from it. Most of the silver is used in jewelry and cutlery. Silver is also widely used in the chemical and food industries. The use of silver iodide is interesting. With its help you can control the weather. By spraying tiny amounts of silver iodide from an airplane, they achieve the formation of water droplets, i.e. in other words, it causes rain. If necessary, you can perform the opposite task when rain is completely unnecessary, for example, during some very important event. To do this, silver iodide is sprayed tens of kilometers away from the event site, then rain will fall there, and dry weather will occur in the desired place. Silver is widely used in medicine. It is used as dentures, in the production of medicines (collargol, protargol, lapis, etc.) and medical instruments.
Silver table service
Elements of the periodic table
Alkali and alkaline earth elements
These include elements from the first and second groups of the periodic table. Alkali metals from the first group are soft metals, silver in color, easy to cut with a knife. They all have a single electron in their outer shell and react perfectly. Alkaline earth metals from the second group also have a silvery tint. Two electrons are placed at the outer level, and, accordingly, these metals interact less readily with other elements. Compared to alkali metals, alkaline earth metals melt and boil at higher temperatures.
| Alkali metals | Alkaline earth metals |
| Lithium Li 3 | Beryllium Be 4 |
| Sodium Na 11 | Magnesium Mg 12 |
| Potassium K 19 | Calcium Ca 20 |
| Rubidium Rb 37 | Strontium Sr 38 |
| Cesium Cs 55 | Barium Ba 56 |
| France Fr 87 | Radium Ra 88 |
Lanthanides (rare earth elements) and actinides
Lanthanides are a group of elements originally found in rare minerals; hence their name "rare earth" elements. Subsequently, it turned out that these elements are not as rare as initially thought, and therefore the name lanthanides was given to rare earth elements. Lanthanides and actinides occupy two blocks, which are located under the main table of elements. Both groups include metals; all lanthanides (except promethium) are non-radioactive; actinides, on the contrary, are radioactive.
| Lanthanides | Actinides |
| Lantan La 57 | Actinium Ac 89 |
| Cerium Ce 58 | Thorium Th 90 |
| Praseodymium Pr 59 | Protactinium Pa 91 |
| Neodymium Nd 60 | Uranium U 92 |
| Promethium Pm 61 | Neptunium Np 93 |
| Samaria Sm 62 | Plutonium Pu 94 |
| Europium Eu 63 | Americium Am 95 |
| Gadolinium Gd 64 | Curium Cm 96 |
| Terbium Tb 65 | Berkeley Bk 97 |
| Dysprosium Dy 66 | California Cf 98 |
| Holmium Ho 67 | Einsteinium Es 99 |
| Erbium Er 68 | Fermium Fm 100 |
| Thulium Tm 69 | Mendelevium Md 101 |
| Ytterbium Yb 70 | Nobelium No. 102 |
Chemical compounds
To form a compound such as silver chromate, chromic acid and the noble metal itself are required. The reaction is not common in nature and occurs much more often in laboratory conditions. If silver is stored in the laboratory, the formula of this substance is immediately recorded on an electronic storage medium.
Silver chromate appears as reddish, rhombic crystals. They are almost insoluble in water and have paramagnetic properties.
When interacting with fluorine, silver fluoride is formed. This substance is considered a binary compound of inorganic origin. It should be noted that this substance is practically not used in industry. Silver fluoride appears as a brownish-green powder. It can also have a crystalline form. This difference is due to the difference in the aggregate states of the original components. In such cases, silver sulfate may even be released.
Decoration and household use
For the manufacture of jewelry or other products, ingots with a silver content of 99.9% to 99.99% are used. The most expensive are products with 925 purity.
The metal is widely used in most industries:
- mechanical engineering;
- instrument making;
- production of photo and video equipment;
- electronics;
- electrical engineering;
- coinage;
- medicine.
The metal has high electrical and thermal conductivity, which is a very important property in the production of parts.
To create jewelry, native silver with admixtures of copper and nickel is used. Well-known brands treat silver items with white rhodium so that they do not lose their original shine and appearance.
There are a large number of brands for making silver products, each has its own specialization, some make watches, others make rings, earrings, others make figures and figurines. Among them:
- AGNI;
- Damiani;
- Boucheron;
- Akvamarin;
- Argentina Bortolotti;
- Balmain;
- Tiffany and Co;
- Gava.Cool;
- Cote and Jeunot by Lena Yastreb;
- Cartier SA;
- Bvlgari (Bulgari);
- Baraka;
- Gucci.
Metal cleaning
- The ore is placed in a tank and treated with zinc dust. As a result, all impurities settle to the bottom, while the target raw material remains at the top. Subsequent cleaning is carried out in factories.
- The pyrometallurgical method produces pure silver. Copper or lead should be used as concentrators. These substances are treated with zinc at a temperature of 450 degrees - this way the metal particles dissolve better. After extracting the frozen substance, the precious metal is separated from it.
- At 1250 degrees, the zinc evaporates, but the remaining silver still contains arsenic and lead. For cleaning, oxygen treatment and heat exposure of 1000 degrees are used. This method is the most profitable, since lead and copper are mined in large quantities. Recycling such elements does not require significant costs.
- The purified precious metal is melted into ingots. No technology can guarantee 100% pure silver. To completely get rid of impurities, the ingots are transported to metallurgical plants for further processing.
If copper or lead is used as the main raw material, a pyrometallurgical purification technique is used. This method is advantageous because these impurities are inexpensive. As a result, the cost of the production process decreases, and the costs of producing less expensive metals are recouped. Electrochemical purification technology is used to separate silver.
Photographic equipment and electronics
The use of silver nitrate and halide for making photographs has recently lost its relevance, because with the advent of digital technology, the demand for color film began to fall rapidly. Global demand for photographic silver peaked in 1999. Now, outdated film photographic equipment is gradually disappearing even in third world countries.
In electrical products, this metal is used for its excellent conductivity. Some electrical manufacturers produce connecting, power and speaker cables using the highest quality silver conductors.
Their conductivity is 6% higher than that of identical copper analogues, but they are also noticeably more expensive. Oddly enough, the demand for such products is quite high. Many audiophile enthusiasts claim that such conductors in audio systems improve sound quality, but this has not been scientifically proven.
Small devices such as watches and hearing aids typically use silver batteries. The reason is that the mass of this metal is relatively small, and its energy-saving properties are very good. It is also used to make silver-zinc and silver-cadmium batteries. In addition, cadmium silver oxide is used in high-voltage contacts.
Combinations with stones and other metals
Jewelers combine silver with many expensive and cheap metals; more often, when making jewelry, they combine gold and platinum with it. There are also no exceptions for setting precious, semi-precious or ornamental stones in silver. World brands set rubies, pearls, emeralds, diamonds in silver; lesser-known factories and companies set cubic zirconia, garnet, amber and other stones.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Silver jewelry goes with any outfit. The same cannot be said about gold. Gold items can ruin a person's appearance. It often overshadows the appearance of clothing, attracting increased attention.
- It is customary to wear gold jewelry for large celebrations and ceremonies. Silver is suitable for any holiday, business meeting, interview.
- Silver jewelry is suitable for both men and women. There are no predominant factors for gender differences.
- Durability, strength, wear resistance.
This metal has no serious drawbacks, except that it darkens over time.
The effect of silver on humans
As we saw above, the use of small doses of silver has a disinfecting and bactericidal effect. However, what is beneficial in small doses is very often harmful in large doses. Silver is no exception here. An increase in the concentration of silver in the body can cause a decrease in immunity, damage to the kidneys and liver, thyroid gland and brain. In medicine, cases of mental disorders due to silver poisoning have been described. Long-term intake of silver into the body in small doses leads to the development of argyria. The metal is gradually deposited in the tissues of organs and gives them a greenish or bluish color, this effect is especially visible on the skin. In severe cases of argyria, the skin darkens so much that it resembles the skin of Africans. Apart from the cosmetic effect, argyria does not otherwise cause any deterioration in well-being or disruption of the body’s functioning. But there is also a plus here, given that the body is saturated with silver, it does not care about any infectious diseases!
American Paul Carson "Papa Smurf", who suffered from argyria