Diamond is a mineral of natural origin. The very name of this stone means “hard”, and many stories about its value and beauty have long turned into legends. Among you, lovers of precious and semi-precious stones, there are probably those who want to know everything about diamonds - including what a diamond looks like in its natural environment and after professional processing by jewelers.
From the history of diamond
Diamond stones were first mentioned around the third millennium BC, but they began to be used as jewelry relatively recently - less than 500 years ago, when jewelry craftsmen began to master the technique of cutting this stone, allowing it to be made into a diamond. Read more about the difference between a diamond and a diamond →
It is known that the Russian Empress Catherine II was very fond of precious stones: diamond, of course, gained her special favor as the most beautiful of all minerals, and the word “diamond” in Russian colloquial use quickly became synonymous with luxury, prosperity and wealth.
This may seem strange, but the exact time when the diamond was discovered cannot yet be established. It is generally accepted that this stone is one of the most beautiful and luxurious in appearance, but this is a generally accepted misconception that has little to do with reality.
A natural diamond, not processed by man, often does not even look like a precious stone, but looks like crystalline rock crystal of an indeterminate shape. Diamond in nature is often colorless or transparent, and the untrained eye does not always recognize in it the very type of stone that can turn out to be an invaluable specimen for a good specialist.
In different languages, the hardness of a diamond is expressed almost the same way. In Arabic it sounds like “almas”, that is, “hardest of all.” In Greek, the description of this stone is expressed by the word “adamas”, which means “indestructible”. In the Russian language, the concept of “diamond” was first heard from the famous traveler Afanasy Nikitin in the 15th century, which was described in the famous literary work “Walking across Three Seas.”
Zodiac signs
Among the zodiac signs there are almost no people for whom this stone is not suitable, except that a diamond can be detrimental to Pisces.
Diamond is most suitable for fire signs and Libra.
- Aries are in complete harmony with the diamond, becoming even bolder and even luckier.
- Leos will become more balanced and feel harmony in their souls and around them.
- It will help Sagittarians achieve success.
- Libra will get rid of indecisiveness and learn to take responsibility.
Is there anything harder in nature?
The hardness of diamond stone has long been known, and it is believed that it has no equal in this regard. However, curious humanity has long been asking the question: maybe there is some kind of rock or other minerals in nature that could compete with a diamond in terms of its legendary “indestructibility”?
I would like to immediately assure everyone who is interested: diamond is the hardest mineral, and there really is no equal to it in this area. It fully lives up to its name, and only it itself can become harder if it is processed using a special method.
What determines the hardness for which diamond stones are so famous? This indicator directly depends on the composition of their crystal lattice. If the crystal lattice is processed using a certain method, removing all possible defects from it, then it is possible to obtain a new laboratory substance called “hyperdiamond” synthetically. This is a diamond whose crystal is so perfect that its strength is eleven times that of natural material. The basis was the type of durable “lattice” that was given to scientists by a rare variety of diamond called “carbonado”: a black stone. About the black diamond →
As you know, ordinary single-crystal (or single-crystal) diamonds are imperfect and have many natural flaws and cracks. It happens that they cannot withstand very high temperatures and pressure. But after specialists were able to reproduce the polycrystalline structure of carbonado in laboratory conditions, we can say with confidence that there is definitely no stone harder than such a material. It can be used to create products of a wide variety of sizes and shapes, which are extremely resistant to any temperature conditions.
Features of the mineral
The structure of diamond is simple: only carbon, but at the same time it is the top of the Mohs hardness scale, while graphite, consisting of the same carbon, is soft and easily broken. The difference lies in the crystal lattice; in diamond it resembles a cube. Diamond cannot be scratched.
This stone, although hard, is also very fragile. It is enough to hit it hard enough for it to split into many pieces. For this reason, in ancient times it was not used to make weapons, like jade (which is more resistant to splitting due to its high toughness).
Diamond has high rates of light refraction and dispersion (scattering) of light, so even a colorless rough diamond shimmers with all the colors of the rainbow (let alone cut diamonds).
Diamond is resistant to high temperatures (burns at 850-1000 degrees Celsius), strong acids and high pressure.
A unique property is luminescence. Also, this stone cannot be seen on x-rays, but it glows bright blue under ultraviolet light.
Composition and properties of the stone
Diamond stone is of carbon origin. Its most common type is a transparent diamond, which can be either colorless or have certain shades of one color or another, giving it a special attractiveness. The shine of a diamond in the sun is very bright - probably, it was this that once attracted a person to itself, prompting him to start using different types of diamonds as jewelry, and subsequently to create unique diamond specimens that received a magnificent man-made cut.
The atoms of the crystal lattice of the stone are cubic in shape. This is the reason for the high hardness ratings: the Mohs scale gives it the highest rating of ten points. But there is one subtlety that at one time craftsmen could not take into account: this is the so-called perfect cleavage, due to which diamond crystals, despite their strength, are very fragile . It was this paradoxical property that often caused valuable types of diamond to be destroyed.
As already mentioned, diamonds, the natural properties of which have not been enhanced by the hand of a good master jeweler, look very modest and sometimes even inconspicuous. What does a diamond just found in a particular deposit look like? Usually, it is a small petrified conglomerate, the surface of which looks matte, and if you pick it up, you can immediately feel a pleasant roughness.
Diamond crystals are more often found as single (or isolated), but there are also fused specimens, which are fine-crystalline formations, or varieties of larger diamonds.
Diamond magic
The magical properties of the diamond were based primarily on the fact that it promised its owner unlimited strength and power. Diamond delivered from evil spells, slander and slander, damage and the evil eye. The magic of the diamond protected spouses from mutual infidelity and saved innocent people in court. When unjust guilty verdicts were passed, the diamond, with its bright shine, confirmed the innocence of the defendant and dimmed when he was guilty.
Diamonds, the value of which among other jewelry was truly enormous, were a symbol of royal power, adorning the crowns of all European and Russian monarchs, and even newborns in royal families were showered with them in hopes of good luck and happiness.
People believed that a diamond amulet would protect them from poisons and could help with poisoning. The custom of wearing a diamond on the ring finger of the left hand came from ancient Egypt. It was believed that this finger is connected to the heart, and wearing a stone on it eliminates malfunctions of the cardiovascular system.
Diamond relieves fatigue and restores vital energy, helps normalize the functioning of the heart and blood vessels
Where and how are they formed
There are several theories about how different types of diamonds are formed. The most reasonable and logical of them is the magmatic theory . If you rely on it, then carbon atoms under the influence of high pressure (at least fifty thousand atmospheres) can change the structure of their crystal lattice, forming this wonderful stone. Moreover, its depth is 100 km or more. Subsequently, during volcanic eruptions, diamonds are carried by magma to the surface of the Earth.
The classification of diamonds, which sorts them based on crystal shapes, color index and other properties, identifies the most interesting meteorite types of these stones. It is likely that this type of diamond is of unearthly origin and arose even before the Sun appeared in our Galaxy. There is also evidence that in nature there are crystals that formed on falling meteorites due to the action of enormous pressure and temperature factors on them.
A remarkable fact is that any types of diamonds are nothing more than “close relatives” of graphite, which undergoes crystallization processes in the bowels of the Earth under high pressure and temperature at great depths. When volcanic lava throws up stones already “prepared” by nature, kimberlite pipes are formed: this is the name of all primary diamond deposits.
When a meteorite falls on Earth, the temperature at the moment it hits its surface is 3000°C, and the pressure rises to 100 hPa. Since such extreme conditions are close in numbers to the processes that occur in the depths of our planet, this becomes the real basis for the formation of an impact type of rock, which includes diamond crystals.
Stones that are clearly of extraterrestrial origin have been found in large quantities in the United States - in the same Grand Canyon where a huge meteorite fell 30,000 years ago. There is a similar deposit, which appeared as a result of a meteorite fall, in Yakutia. Such large meteorite craters are called astroblemes and are found in different parts of the Earth: in addition to the USA and Yakutia, a similar deposit in the form of a crater is found in the northern regions of Siberia.
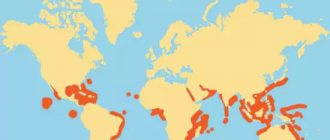
Despite its obvious rarity, diamond is a stone that is very widely distributed. Its deposits can be found everywhere except Antarctica. Read more about how diamonds are mined →
Variety of shapes and sizes
Diamond is a stone with very diverse morphological characteristics. The shape of diamond can be either mono- or polycrystalline, which directly determines the strength indicator. The already mentioned black carbonado has a polycrystalline structure, which was copied by scientists in the laboratory to synthetically produce a super-strong stone. Kimberlite deposits are represented exclusively by those diamonds whose shape is an octahedron or flat-edge.
There are also complex crystals with the original shape of rhombuses or cubes, among which there are specimens that have typical shapes with rounded edges - rhombodecaedroids. They occur when diamonds dissolve under the influence of kimberlite melt. As for the cuboid type of crystals, their formation is ensured by the fibrous growth of diamonds, which occurs according to the normal mechanism. By the way, laboratory-grown diamonds are most often characterized by cuboid crystals, which is one of their differences from natural stones.
The crystals of different diamonds vary: from those that can only be seen under a microscope to very large ones. For example, in 1905, a specimen weighing 0.621 kg, which is 3106 carats, was discovered in South Africa . It was studied for several months and then split into several parts. Rare stones are those whose weight exceeds 15 carats, and the rarest are those whose weight is 100 carats or more. As a rule, they certainly occupy a special place in history, and they are even given names. How to find out how many carats are in a diamond →
Price
A cut diamond is a very expensive gemstone.
Diamonds are graded using the 4C system:
- cut —cut;
- clarity - purity;
- color — color;
- carat - weight in carats.
This helps determine how close a given specimen is to perfection.
The cost of a carat of a colorless diamond without colors or defects, with a standard cut, is about $1,000 .
Of the colored diamonds, the most expensive are red and black, while green and blue are slightly less expensive.
Examples of prices in Russian online stores:
- necklace with 1 diamond (14k white gold) — RUB 22,300. ;
- diamond pendant (14k white gold, product weight 1.39 g) - RUB 33,660. ;
- ring (14k red gold, ring weight 2.55 g) - RUB 36,950. ;
- diamond (0.41 carat) - RUB 69,990.
Color spectrum
What colors are diamonds? Depending on the impurities contained within them, as well as the characteristics of the chemical reactions that occurred during the formation of the stone, the color of the diamond may vary.
A stone that does not have any colors is of extraordinary beauty; the transparency of a diamond of this type is sometimes figuratively characterized by the famous phrase “pure water diamond.” Most often, specimens have a slight tint of some color or “color.” Stones of “pure water” are the least common among them.
Yellow colored diamonds are formed when the carbon atoms present in their crystal lattice are replaced by nitrogen particles. It will be fair to talk about what color exactly yellow stones are, because their shades are numerous, and they come across quite often. The highest value is found in dark yellow stones, which look best cut in pure gold.
There is a stone that is valued even higher than the legendary “pure water”. If you ask experts what color diamonds are valued more, the answer will be red. They are mined in Australia, in very deep deposits. Pink diamonds are also mined in Australia and are more common.
A diamond, the color of which is called “brown,” can have literally all its possible shades: chocolate, cognac, amber, champagne. These are the commercial names that these stones are used by jewelers. Read more about cognac diamonds →
The process of formation of red, pink and brown stones has not yet been fully studied, which gives them a peculiar mysticism and attractiveness
If we are talking about a blue stone, a diamond with this color has long earned the title of auction and unique. Its blue color is given by the substitution of atoms in the crystal lattice from carbon to boron. Refining natural diamonds with blue color is often practiced by specialists and in laboratory conditions.
Also no less rare are blue diamonds, the mission of which is to represent the most valuable private collections. However, the technology of “transforming” the more common yellow diamond into blue through man-made chemical reactions has long been used here.
The green color of a diamond is acquired when it is exposed to natural radiation for a long time. These minerals are truly beautiful with their rich dark green hue and receive very high marks from jewelers.
Black diamond lies in the upper layers of the earth's crust, and its lattice structure consists of microscopic crystals fused together. It is extremely beautiful and durable - it has already been mentioned several times in our article.
TYPES OF CUT
Clarity and color of a diamond play a significant role in the value of a diamond, but not the key one. For a nugget to become refined and refined, the skill of the jeweler is important.
We recommend: TOP-13 shades of TOPAZ
In the diamond industry, it is customary to process raw materials in several stages before sending them to the shelves:
- CLEAVING THE CRYSTAL. The diamond is scanned using X-rays, in this way finding damage in it that is invisible to the human eye, which is required to facilitate cutting the diamond.
- REARING OF MINERALS using a lathe. The process is designed to form edges and corners on the stone.
- TREATMENT. The process takes place on iron polishing wheels, which are sprinkled with special diamond powder. The procedure ensures deep cutting of the mineral.
- POLISHING. A final treatment process that allows the stone to shine brighter and deeper.
Manufacturers use several shapes in the diamond cutting process. The specific design of the jewelry determines how the potential of the stones will be revealed. Any cut must meet the requirements for size and angles of inclination.
Color and purity table
The following classical methods of stone cutting are distinguished:
- ROUND. Tolkovsky's invention. Since then, the round cut has been the most popular and versatile. However, during the process the material is subjected to merciless processing, as a result of which the mineral loses most of its weight.
- PRINCESS. Square shape with sharp corners. When grinding, a minimum amount of waste is observed.
- PEAR. The sophisticated shape looks good with earrings, pendants and rings. A pear-shaped stone visually lengthens your fingers.
- MARQUISE. The elongated boat shape adds charm, aristocracy, and sophistication to a woman.
- OVAL. The oval shape of the stone creates an emphasis on the desired part of the body: ears, neckline, hands.
- HEART. Processing the heart shape requires multi-step, complex work. Therefore, such stones are more expensive than others.
- EMERALD. The shape of the stone is rectangular, with an octagonal cut. A less common option due to the extraordinary refraction of light.
- USHER. Square shape, multi-stage, with multi-tiered refraction of light.
Jewelers are working on creating other cuts, using different processing technologies.
Application
Rough diamonds of good quality and shape are always highly valued in the jewelry community. A diamond is a diamond that has been processed (or cut) by a specialist, resulting in a shape that will best reveal its brilliance and color splendor.
Small and very small stones, which are not suitable for cutting, are used to make diamond drills, which are used to process granite and other high-strength rocks. By the way, it is the famous black carbonado diamond that is most valued in the industrial sphere for the manufacture of expensive and high-quality tools. About the use of diamonds →
How to distinguish a real diamond from a fake
The development of the chemical industry gives scope for the spread of skillfully made fakes or imitations, many of which enjoy a certain success among buyers due to their brightness and low cost.
However, it is always possible to distinguish natural stone from man-made:
- For example, a natural diamond has the ability to strongly scatter light . If you direct a light beam through a stone and it does not change its direction and remains uniform, it is definitely a fake.
- A natural diamond begins to glow when exposed to ultraviolet rays .
- Known for its durability, real diamond is resistant to abrasion . In this regard, it makes sense to carefully examine all its faces through a magnifying glass: if they have scratches, cracks or abrasions, the stone is fake.
- If conditions allow, you can draw a marker along the edge of the stone . If the line is straight and does not blur , the diamond is most likely real.
- Natural stone does not fog up if you breathe lightly on it.
- There is also a very “barbaric” but useful experience of immersing a diamond in acid - if it is not a fake, then nothing will happen to it .
Cubic zirconias are often passed off as diamonds - artificial stones developed at the Lebedev Physical Institute almost fifty years ago. It can be difficult to distinguish it from natural stone, but here you should pay attention to the number of edges. A diamond has a standard number of 57, while fakes have much less. Typically, such an experiment is carried out through a magnifying glass with 12x magnification. Read more about how to distinguish a diamond from cubic zirconia →
Diamond is a wonderful stone that will always be valued among amateurs and professionals in jewelry, and if you know how to distinguish a natural mineral from a fake and know how to identify a diamond for authenticity, you have a chance to purchase good quality jewelry that will serve you for a long time. for many years.