Stones are cut to give them a certain shape, to emphasize the shine and play of light. A high-quality cut prevents rays from passing through - they are refracted in the edges of transparent and translucent stones and come back out. First, a scheme is created and thought through, taking into account the shape of the stone, the number, size and location of the edges and angles between the edges. The stones are then cut and polished.
There are about 250 varieties of cuts in jewelry. They depend not only on the taste preferences of jewelers, but also on the physical and optical characteristics of the stones. During the cutting process, it is important to preserve the weight of the stone and its natural advantages. Cutting can be divided into three large groups: smooth , faceted and mixed .
Smooth cut
Although formally it is classified as cutting, in essence it is polishing. The stone processed in this way has no edges, only a polished surface.
Cabochon (from the French caboche - “head” or “nail with a wide and round head”) is the most famous type of smooth cut. The cabochon is considered one of the first, and therefore the oldest, cuts. Honed stone usually has a flat bottom and a smooth, convex dome. Most often it is made in the shape of a circle or oval, although other shapes are also found: rectangle, rhombus, heart, drop, boat, crescent.
Cabochon cutting is used for opaque and translucent stones, as well as for stones with various optical effects (asterism, iridescence, opalescence, cat's eye). This is how jade, turquoise, amber, malachite, lapis lazuli, serpentine, onyx, opal, tugtupite, and sometimes sapphires, rubies and other stones are processed. This cutting method is not very complicated, and the quality of the source material does not play a big role.
Different types of cabochons are used for different tasks and stones. Opaque stones with a colored surface are cut into a single cabochon, which has a flat base and a convex top. For stones with internal defects, the shape of a double (lentil) cabochon, in which both sides are convex, is suitable. Dark stones are often cut into hollow cabochons with a concave base. There is also a tall cabochon with a very convex top and a flat one that looks like a frozen drop of candle wax.
Ball is another smooth cut option.
Semi-precious and ornamental stones are processed in this way: aventurine, agate, amethyst, quartz, malachite, onyx, jasper.
The need for stone processing
During cutting, precious and semi-precious stones acquire the required shape. The jeweler must take into account the condition of the material - its design, composition, original dimensions. As a result, an unsightly-looking pebble turns into a beautiful product with a smooth surface and clear edges.
The way the stone plays in sunlight depends on the processing method. The highlights shimmer over the edges and give them a special shine . There may be different types of cutting of gemstones, but the craftsman takes into account the shape he gives to the mineral and the type of facets.
It is difficult to achieve the ideal appearance of a crystal; it takes a lot of time and effort. The jeweler uses many special tools, creating from 30 to 240 facets on one stone. They are called beveled and must have a perfectly smooth surface and precise angles.
Faceted cut
The most diverse type of cut is faceted or beveled (from the French facette - “edge”). As the name suggests, this treatment creates many edges on the surface of the stone. Faceted cutting is used when working with transparent stones: it brings out their shine, enhances color and emphasizes light effects.
To understand the features of different facet cutting options, you need to understand the anatomy of a faceted stone.
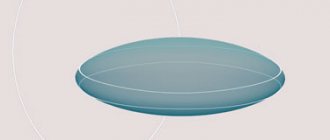
Scheme 1: structure of a cut stone
The upper and lower parts of the stone are separated by a thin belt - a girdle. Usually the frame is fixed on it. The upper part, located above the girdle, is called the crown. There is a platform on it - a flat top face, the largest face of the stone. The lower part, located under the girdle, is called the pavilion. And the point of convergence of the edges of the pavilion at the very bottom is a culet; it can be in the form of a spike, a small horizontal edge or a line.
The faceted cut is divided into two types: classic or round brilliant , and fancy .
Color options
It’s strange to ask what color an emerald is - everyone knows this!
However, there are emeralds of other shades:
- Red emerald. Beryls with crimson-red hues are rare in nature, which is why they cost twice as much as the usual green ones.
- Pink. Beryls received soft pink shades thanks to manganese cations. They are called emeralds, although officially, given their mineral composition, they do not belong to this family and in Russia they are called sparrows.
- Copper emerald. In fact, it is dioptase, which they are trying to pass off as an emerald.
- Black. It was mentioned above - this is the Trapiche emerald. It looks like an orange with a black peel and green segments.
- Blue emerald. A rare species, most often found in artificial form.
Faceted: round diamond
The round brilliant cut is the most common form of cutting for diamonds and other clear stones with strong light dispersion.
The pioneers of the round shape are considered to be the Americans Henry Morse and Charles Field, who in the 1870s created a steam engine for processing diamonds.
The round cut best demonstrates the brilliance and play of light in the stone and minimizes the risk of external damage. A diamond sparkles brightest if the exact proportions of the pavilion's edges are met - they are the ones who ensure complete internal reflection of light. The main disadvantage of the round cut is the significant loss of weight of the nugget: after processing, up to 60% of the original weight can be lost.
The classic or full brilliant cut consists of 57 facets. There are 33 facets on the crown and 24 facets on the pavilion. First of all, this cut is used for large diamonds weighing over 1 carat. The main role here is played by proportions, symmetry and surface quality. The standard of a classic cut is considered to be the “ideal diamond,” the parameters of which were calculated by mathematician Marcel Tolkowsky in 1919.
The simplified brilliant cut consists of 33 or 17 facets. It is used when processing small and medium-sized stones: 33 facets for stones weighing up to 0.99 carats, 17 facets for “diamond chips” weighing up to 0.29 carats. Diamonds, rhodolites, amethysts, sapphires, rubies, peridots, topazes and many other stones are processed in this way.
Photo 1: classic or full diamond cut, the author of this and other photographs is Dmitry Stolyarevich
Types of round cuts that have more than 57 facets are called diamond modifications. These are, for example, the Belgian Highlight (73 facets), King (86 facets) and Magna (102 facets) developed in New York, or the Royal Cut (154 facets).
Healing powers
King Solomon spoke about the healing power of the stone several thousand years ago. He believed that emerald could remove poison from the body, heal night blindness, and heal open wounds.
This stone has other abilities:
- help with dysentery, psoriasis, diabetes;
- temperature drop;
- treatment of burns and inflammations;
- improving the quality of vision;
- help in the fight against epileptic seizures;
- treatment of depression and insomnia.
With the help of the gem they fight melancholy, fatigue and nervousness. They say that it helps with joint pain and gastrointestinal diseases.
Attention! This text does not constitute medical indications for treatment. Take care of yourself, do not forget to consult a doctor on time.
Faceted: fantasy. Step varieties
With this cut, the edges are arranged parallel and above each other, like steps. The wide upper platform is made in the form of a polygon, and the side faces are in the form of trapezoids or isosceles triangles.
The step cut does not cause brilliant shine, but rather emphasizes the color of the stone. Therefore, it is used for transparent stones of “medium color tones”: a high cut enhances the color, a low cut weakens it.
The table or table cut is one of the simplest step cuts. Usually it is a flat stone with a large platform: the crown consists of five sides, the pavilion - of four. A variation can be considered the Mirror cut with a very large platform and a shallow pavilion. The table is used mainly for semi-precious and ornamental stones, which are often used in signet rings.
Baguette is an elongated version of the Table, cut in the shape of a rectangle. Shapes such as Trapezium and Square (Care) are often classified as varieties of Baguette.
The modern version of this cut appeared in the early 20th century. Its name comes from the French. bague – Until the 17th century, this word meant precious stones in general. The Baguette has 14 sides, and there are also 24-sided versions. Technically it is quite simple, but due to the openness of the edges it requires high purity of the stone. This is how small side stones in jewelry are mainly cut: diamonds, rubies, emeralds, topazes.
Other quadrangles - Rhombus, Kite, Epaulet, Barrel - are considered varieties of Baguette. They are distinguished by the inclination of the corners and the curvature of the sides. Pentagon and Hexagon are also distinguished as independent forms.
Emerald (Emerald) or Octagon - a step cut with an octagonal shape of the stone. It consists of 58 or 65 edges and looks like a Baguette, but the corners here are not sharp, but beveled.
Modern Emerald standards were adopted in the 1940s - initially this cut was intended specifically for emeralds, but over time, sapphires, tourmalines, beryls, and other stones began to be cut this way. Here, too, high purity and transparency of the stone is required, otherwise imperfections will be visible to the naked eye. But the light that falls on the surface is reflected in wide and bright flashes. In terms of cost and complexity, this is one of the most affordable cuts.
Asscher is an octagonal cut, which is made in the shape of a square and has characteristics similar to Emerald. It was developed in 1902 by the famous Dutch jeweler Joseph Asscher, but it gained popularity only in the 1920s. The original version has 58 edges, and its modification, the Royal Asscher, has 74 edges.
Photo 2: emerald cut
Photo 3: Asscher cut
Jewelry examples
Rings, earrings, and necklaces are encrusted with emerald-cut stones. One of the most striking examples of emerald-cut jewelry is Meghan Markle’s aquamarine ring, given to her by Prince Harry on the eve of her wedding. At one time, this jewelry belonged to Princess Diana.
The most expensive ring from the collection of actress Elizabeth Taylor, a big fan of jewelry, has the same cut. The diamond, a gift from my husband, weighs 33.19 carats. The actress was also the owner of the luxurious BVLGARI Cleopatra demi-parure, which features an emerald-cut Colombian emerald necklace.
Faceted: fantasy. Wedge varieties
Wedge cut shapes are often considered variations of the round brilliant cut. In this case, many edges in the form of wedges are applied to the surface, which well reveal the color of the stone and enliven the play of light in it.
Oval – this cut compares favorably with round by maintaining the weight of the stone. It was created in the 1960s by jeweler Lazar Kaplan. Oval-cut stones usually have 57 facets, although the number may vary. The elongated shape allows you to create the illusion of a larger stone; it looks especially advantageous in rings. The oval cut is used mainly for large transparent stones - aquamarines, amethysts, sapphires, topaz.
Marquis (Marquise) is an oval with pointed ends, similar to a boat. This cut was created in France in the mid-18th century, and according to legend, it was dedicated to the smile of the Marquise de Pompadour. The marquise also has 57 facets and is characterized by a slight loss in the weight of the nugget: if the stone is initially oblong, up to 80% can be preserved. This is how diamonds, amethysts, emeralds, and rubies are cut. The Shuttle cut is considered a variation of the Marquise - it has a narrower upper platform and slightly fewer facets.
Photo 3: oval cut
Photo 5: marquise cut
Pear – this cut visually resembles a drop: one end is rounded, the other is pointed. It is sometimes considered a hybrid of the round brilliant cut and the marquise cut. The smooth platform is also made in the shape of a drop, there are usually 57 wedge faces. Such a stone should have clear symmetry at the point of narrowing, since this is where the play of light is concentrated.
Aquamarines, amethysts, and topazes are cut in the shape of a Pear. The Pandelok cut is a variation of the Pear, but its pavilion is deeper and rounder.
Briolette, Drop, Olive (Olive) - varieties of elongated teardrop shape. Unlike Grusha, they have neither a platform nor a girdle. The surfaces of Briolette and Olive are completely covered with wedges, only the shape of the Olive resembles an ellipse with cut ends. In the Drop, the narrow upper part is formed by long edges extended downwards, and the rounded lower part is formed by small wedges. Stones cut in this way are mainly used as pendants.
In elongated Oval, Marquise, and Pear cuts, if the proportions and symmetry are disturbed, the optical effect of a “bow tie” may appear: a dark spot in the center of the table.
Photo 5: pear cut
The Princess is a rectangular wedge cut and is the second most popular cut for diamonds. It was created in the 1980s by jeweler Bezalel Ambar - he branded the original version with 49 facets under the name Quadrillion. The princess has square outlines and sharp corners, and the deep pavilion, where the play of light is concentrated, ends in a spike. The 58 facets create a brilliance that rivals round diamonds, but retains about 80% of the stone after cutting.
Flanders is a modification of the Princess, which has 61 sides. It was also invented in the 1980s, named after the Belgian region of Flanders. Features cut corners and very complex symmetry, so the cutting process takes three times longer than creating a round diamond.
Photo 6: princess cut
Antique (Antique) or Cushion (Cushion) - this cut has existed for more than a hundred years and at one time was almost as popular as round brilliant diamonds are today. The shape of the Cushion (English cushion - “pillow”) really resembles a pillow. The stone has rounded corners, 72 sides, and can be square or slightly elongated. This is how diamonds, amethysts, sapphires, emeralds, rubies, quartz and its varieties are cut. By the way, the cut received its other name - Antique - in recognition of its historical roots: its predecessor is considered to be the Old Mine Cut of the 18th century.
Trilliant (Trillian, Trillion) is a triangular wedge cut created by the Asscher brothers at the beginning of the 20th century. The corners of the stone can be sharp, beveled or rounded; some options have a pronounced triangular area, some do not. The classic Trilliant has 43 facets, but modern versions can have 50 facets or more. This cut is well suited for light stones: diamond, aquamarine, beryl, white sapphire. Some jewelers use it to lighten dark stones - tanzanite, amethyst, rhodolite. Varieties of the Trilliant can be considered the Shield and Troidia cuts, in which the sides are slightly curved outward.
The heart is one of the most complex and expensive wedge cut shapes. It is often used in exclusive jewelry. In principle, it resembles a Pear, but splits on the rounded side, taking the shape of a heart. The stone is usually equal in length and width, and consists of 59 facets - their number may vary depending on the original size of the stone. This is how rubies, amethysts, topazes, garnets, and sometimes colored diamonds are cut.
Ball or Sphere is a rather rare type of wedge cut, which has 120 facets or more. Despite the fact that a stone processed in this way will not sparkle very brightly, the cutting itself is extremely labor-intensive and requires high skill.
Photo 7: heart cut
Also worth noting is the collection of polygonal “floral” cuts (Fire Rose, Sunflower, Dahlia, Calendula, Zinnia), which were created by the famous jeweler Gabi Tolkowsky, nephew of the creator of the “ideal diamond”. They are designed specifically for rough diamonds over 0.25 carats and are based on unusual angular parameters. Russian experts have developed the Happy decagonal cut, which has 81 facets. Visually, it is very similar to a round diamond, but, like many other fancy options, it has less weight loss from the stone.
History and origin
The history of emeralds begins with Ancient Egypt, where their first deposits were allegedly found. Gems were mined there even under the first pharaohs, but the mines were abandoned by the beginning of the 17th century. Nowadays they are better known as the mines of Queen Cleopatra.
The mines of Colombia, the second oldest mines of the Emeralds, are famous for their bloody history. The area of these deposits was at war for 400 years. The Spaniards discovered the mines thanks to captured Indians, but they were not able to break through to the deposits immediately. Even after the seizure of territories, the Indians rebelled more than once and attacked the mines that came into the possession of the Spaniards. The extracted gems from these mines were transported to Europe.
The largest emerald in the world was found in Brazil: it is called "Bahia", weighs about 400 kg and is worth approximately 400 million dollars.
Criteria for determining quality
To choose the best stone, you need to know how to check its quality. This can be done by specialists with knowledge in this field. The check is performed using professional equipment. But there are basic characteristics that determine the value of an emerald, knowledge of which will help everyone when choosing a stone.
What criteria are considered decisive?
- Color.
- Transparency.
- Origin.
- Cut.
- Weight and size.
Knowledge of all these characteristics will be useful when purchasing products with emeralds.
Zodiac signs
First of all, among those who are suitable according to their zodiac sign, we should name Gemini. He brings them the gift of composure and wisdom. Emerald enhances concentration and strengthens memory. With the help of the stone, it will become easier and more pleasant for Gemini to build contacts with other people. The mineral will remove excessive emotionality and aggression, giving peace in return.
The stone is suitable for Virgos. It helps them control their bad habits, be collected in difficult situations, not despair in case of failures and enjoy the little things.
Emerald is an important stone for Taurus as well. It develops their intuition, helps them achieve their goals faster, and gives them the opportunity to look at the world in a new way, in bright and joyful colors.
This gem is recommended to be worn by Cancers, Sagittarius and Aries to improve their mental abilities. Emerald is contraindicated for Scorpios: it has an unfavorable effect on them.
Place of Birth
Good emeralds are rare, most of them are found in the Colombian deposits of Tunja (the deposit was discovered in 1555) and Muso (known since 1537), in New Granada, Zambia, Brazil and Egypt.
Emeralds of lower quality are found in Habachtal, in Salzburg (Austria), in the Mourne mountains (Ireland), on Lake Mjoesen (Norway) and in some other places. Emeralds are also mined in Russia, USA, Canada, Australia, Spain, France, Switzerland, Italy, Germany, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Pakistan, Afghanistan, India, China, Cambodia, Egypt, Ethiopia, South Africa, Somalia, Nigeria, Namibia, Tanzania, Zimbabwe, Mozambique and Madagascar.
Magic abilities
Emerald has been considered a magical gem since ancient times. Queen Cleopatra singled it out among other precious stones; Polycrates sacrificed it to the gods.
Among his magical abilities are:
- a talisman against committing crimes;
- improving living standards and well-being;
- repelling evil and selfish people from the owner of the stone;
- increases mental abilities;
- gives good luck;
- protects during travel;
- brings peace and satisfaction to life;
- protects marriage bonds;
- gives longevity.
It was called the “stone of prisoners”: a warrior’s gem allowed him to be collected and cold-blooded. The gem did not tolerate infidelity or bad thoughts from its owner, so reliable and kind people possessed it. It helps those who have problems with self-confidence. Occultists use dark emerald when making contact with the dead. It helps women with conception and easy childbirth.
Cost of emeralds
The cost of a cut stone varies due to various factors, from eight to twenty thousand dollars per carat.
1 carat is equal to 0.2 g. The greater the weight of the stone, the more carats it has, and the higher the price. But in the case of emerald, the price is determined not only by weight. This mineral without any defects is very rare, and therefore many stones that weigh more than tens of carats have no significant value due to their defects. In addition to weight, the price of an emerald is influenced by color - it should be rich, dark green. Factors such as transparency and cleanliness also play an important role. The cost of a stone can be influenced by the region in which it was mined, the weight of the stone after cutting, the presence of a certificate from trusted laboratories, the quality of its cutting, the symmetry of the edges and the quality of polishing. Methods used to improve the color and clarity of an initially flawed stone also affect its value.
Experts count up to sixty shades of emerald. In accordance with Russian standards, only five color groups are taken into account.
Today, top quality emeralds are quite rare, and therefore cost significantly more than a diamond of the same carat.
Talismans
Amulets made from the green mineral were popular in Ancient Egypt. Then they believed that this was the stone of the goddess Isis, the patroness of women and the hearth. He helped the calm course of pregnancy and easy childbirth.
Emerald talismans also have other properties:
- In a gold frame, the gem will protect against many diseases, love spells and neuroses.
- The dreams of the owner of the amulet often come true.
- Well suited for love talismans, as it is designed to preserve and protect love couples. If betrayed, it can split.
- The emerald can be hung on the head of the bed: it will protect against nightmares.
- To combat epileptic seizures, it is worn around the neck or in rings.
View this post on Instagram
Publication from ?treat yourself to Serebrom? (@serebro_elitt) January 21, 2019 at 12:20 PST
Only a natural emerald can serve as a talisman: synthesized stones, and especially fake ones, will not bring the desired result.